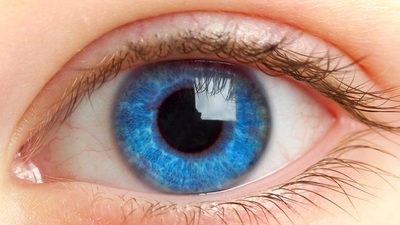
 A startling blue durable pigment called YInMn blue has been licensed for commercial use 7 years since its discovery and it has already found its way into the hands of some artists. Chemist Mas Subramanian and his team discovered the pigment in 2009 at Oregon State University while they were conducting experiments connected to electronics. It is one of those 'happy accidents', an unexpected discovery like Bluetac! With a unique crystal structure the compound doesn't fade, even when exposed to oil or water, and it is environmentally friendly. "Ever since the early Egyptians developed some of the first blue pigments, the pigment industry has been struggling to address problems with safety, toxicity and durability,” said Subramanian (existing blue pigments include ultramarine, made from ground lapis lazuli, and toxic alternatives such as cobalt blue and Prussian blue). "Now it also appears to be a new candidate for energy efficiency,” Subramanian adds, referring to the colour’s ability to reflect light and potentially keep buildings cool. The Shepherd Color Company is involved in commercialising this exciting new pigment. Can you see its vibrant blue hue? Recent evidence suggests that that, until modern times, humans didn't see the colour blue at all! In an interesting article in Business Insider, Kevin Loria breaks down the evidence behind the claim, which dates all the way back to the 1800s when scholar William Gladstone noticed that, in The Odyssey, Homer describes the ocean as 'wine-dark' but he never uses the word 'blue'. Every language first had a word for black and for white, or dark and light. The next word for a colour to come into existence, in every language studied around the world, was red, the colour of blood. After red, yellow appears and then green. Finally blue appears in every language. The only ancient culture with a word for blue was the Egyptians, they were also the only people that had a way to produce a blue dye. So before blue became a common concept we may have seen it, but not known we were seeing it. Blue is rare in nature. Even the sky or bodies of water (like a lake) aren't blue often. Philologist Lazarus Geiger’s research shows that even in scriptures describing 'the heavens' still don’t necessarily see the sky as 'blue'. Jules Davidoff traveled to Namibia to investigate and conducted an experiment with the Himba tribe, who speak a language that has no word for blue or distinction between blue and green. He discovered they couldn't pick out blue from green, but could discern very subtle shades of green that were not visible to most of us. Another study by MIT scientists in 2007 showed that native Russian speakers have a word for light blue (goluboy) and dark blue (siniy), and can discriminate between light and dark shades of blue much faster than English speakers.
Anne
7/5/2016 08:39:24 pm
Reminds me of what we call the Klein blue ? named after artist Yves Klein - http://encycolorpedia.fr/002fa7 Comments are closed.
|
Archives
December 2023
Categories
All
|
Gateway to the Heavens Do you realise you actually shape your destiny and shapes influence your destiny. If you want to understand how this works ask Karen to give a talk about it or read her excellent book. You may have hated even the mention of geometry at school, but Karen's simple and illustrated explanations will give you a real insight into this fascinating topic. |
The Hidden Geometry of Life The attentive audience was enthralled by Karen's introduction to the principals of this truly multi-dimensional topic ... The energy in the room, by the end of the evening, was well and truly charged! |







 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

